
This surgery relieves the pressure on the spinal cord and nerves by removing the lamina, a procedure known as a laminectomy, or by removing the vertebral body, a procedure known as a corpectomy. The surgeon may remove a specific bone that is compressing the spinal cord and nearby nerve roots, which is referred to as a decompression surgery. The treatment must always be specifically tailored to the patient’s presentation the choice of procedure will depend on several factors.

However, surgery is required if the burst fracture has significantly impaired the mechanical strength of the spine or causes compression of the spinal cord or nerves, leading to neurological deficits. has not led to neurological and/or structural compromise, then the doctor may initiate a nonoperative approach.
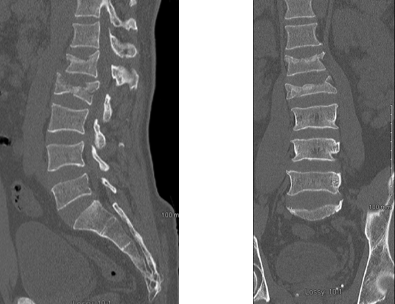
If the burst fracture is not severe, i.e. MRIs can give an accurate picture of the spinal cord.Ī burst fracture is a serious injury it typically requires immediate hospitalization and treatment. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of large magnets, radiofrequencies, and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and structures within the body.CT scans are more detailed than general X-rays. Computed tomography (CT) scan: a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed images of any part of the body, including the bones, muscles, fat, and organs.

Dynamic, or flexion/extension X-rays (X-rays that show the spine in motion) may be obtained to see if there is any abnormal or excessive movement or instability in the spine at the affected levels. Specific bony abnormalities such as bone spurs, disc space narrowing, vertebral body fracture, collapse, or erosion can also be identified on plain film X-rays. Spinal dislocation or slippage (also known as spondylolisthesis), kyphosis, scoliosis, as well as local and overall spine balance. X-rays provide an overall assessment of the bone anatomy as well as the curvature and alignment of the vertebral column. Soft tissue structures such as the spinal cord, spinal nerves, the disc, and ligaments are usually not seen on X-rays, nor on most tumors, vascular malformations, or cysts.

Bone fragments can also be displaced into the spinal canal or foramen (exit route for an individual nerve root), leading to pressure on the nerves and compromised function. In general, a burst fracture represents a serious problem, since the vertebral body shatters with enough force to separate the bone fragments and compromise the vertebra’s ability to support the spine. There are a number of different classification schemes to describe burst fracture and help direct their treatment. Burst fractures account for 14% of all spinal injuries. In a burst fracture, the vertebral body shatters.Ī burst fracture usually results from significant trauma that compresses the bone, such as a motor vehicle accident or a severe fall. The vertebral body is the cylindrical shaped portion of the vertebral bone that lies in front and provides the majority of structural support.
ACUTE L1 COMPRESSION FRACTURE TREATMENT SKIN
You can feel the spinous process, a projection from this arch, when you press on the skin in the middle of your back. The vertebral arch is a ring-shaped section that forms the roof of the spinal canal and protects the spinal cord. The bones of the spine have two main sections. A burst fracture is an injury in which the vertebra, the primary bone of the spine, breaks in multiple directions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
